Top tips:
- The three most common causes of cirrhosis are Metabolic dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), Alcohol and Hepatitis C virus
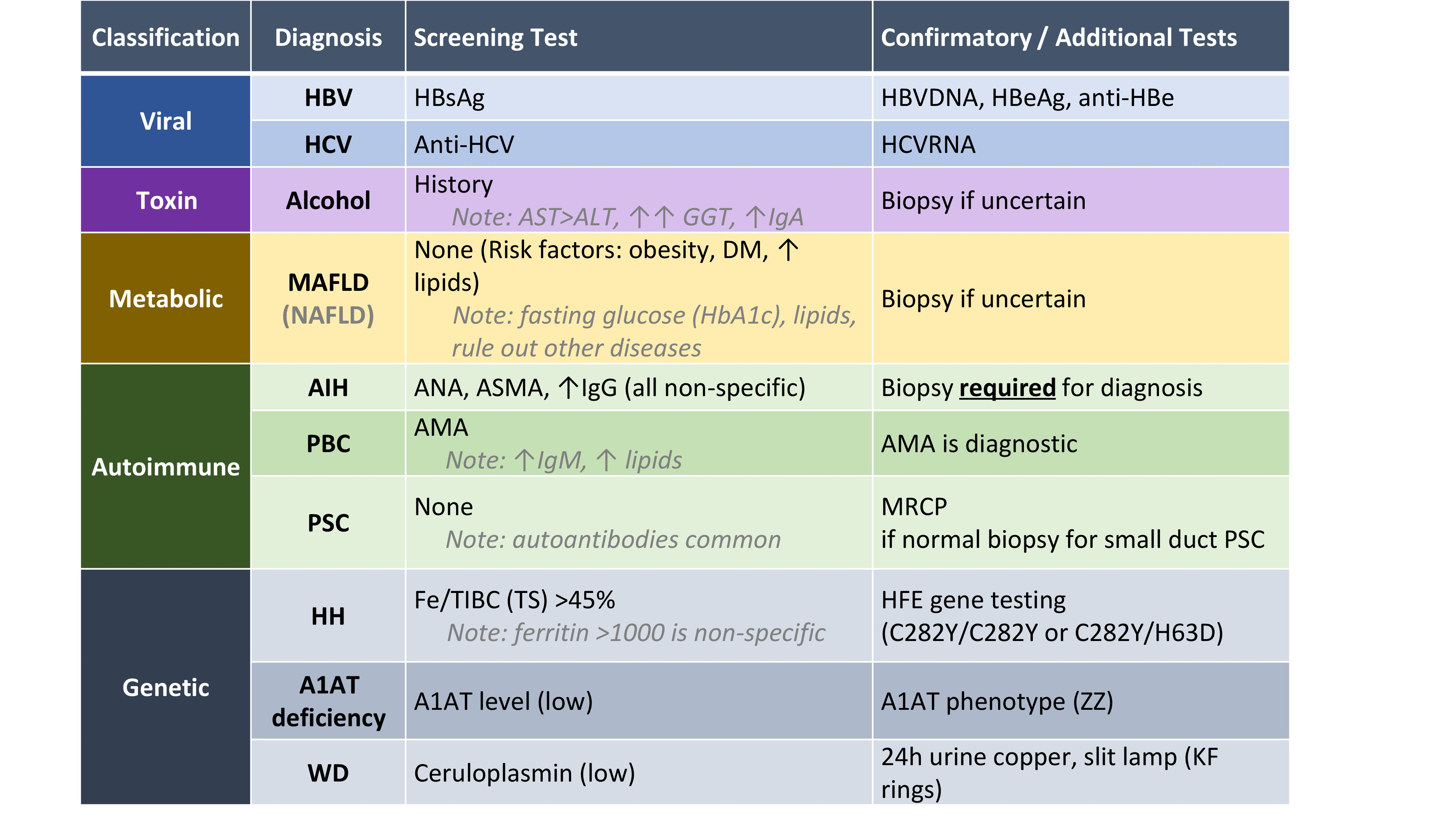
- In addition to a detailed history, examination and liver imaging such as an ultrasound doppler, basic testing in all patients with cirrhosis should include screening with the anti-HCV antibody (will require HCV PCR to confirm diagnosis if antibody is positive), HBsAg, quantitative immunoglobulins and iron studies
Order panels Liver disease work up
For adults:
Liver disease work up

Check out the bottom of the page for a short video from Dr. Zeman!
Cirrhosis Etiologies
Most common:
- Metabolic dysfunction associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- Alcohol related liver disease
- Chronic viral hepatitis (Hepatitis B, C)
Less common causes (not all inclusive):
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis
- Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
- Wilsons disease
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Etiology Considerations
History:
- Alcohol: Alcohol use (>2 standard drinks/day for women and >3 for men where a standard drink is 10-14 grams of alcohol)
- Metabolic dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Diabetes or metabolic syndrome
- Viral hepatitis: Exposures (place of birth, travel, sexual behaviours, drug use, incarceration)
- Medications and supplement use are unlikely to cause cirrhosis, but can contribute to acute deterioration – see link to Livertox website to evaluate risk and injury pattern of high-risk medications or medications started within the previous 6 months.
- Autoimmune hepatitis, Primary biliary cholangitis: Family history or personal history of other autoimmune conditions
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Co-existing Inflammatory bowel disease
- Genetic liver diseases (Wilsons, Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, Hemochromatosis): Family history of cirrhosis (age of onset, etiology), hemochromatosis, premature emphysema
- History of congestive heart disease
Pattern of liver tests:
- Hepatocellular (Predominantly high AST/ALT compared to ALP)
- Cholestatic (Predominantly high ALP compared to AST/ALT)
Link to R-Factor for Liver Injury calculator when you are working up worsening liver enzymes to determine if the pattern is hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed.
Patient materials:
You can direct patients to the following:
Alcohol
References:
This section was adapted from content using the following evidence based resources in combination with expert consensus. The presented information is not intended to replace the independent medical or professional judgment of physicians or other health care providers in the context of individual clinical circumstances to determine a patient’s care.
Authors: Michelle Carbonneau NP, Dr. Marilyn Zeman, Dr. Aldo Montano-Loza, Dr. Kelly Burak, Dr. Puneeta Tandon
Last reviewed December 9, 2022